field class
#include <ldtk_field.h>
Constructors, destructors, conversion operators
Public functions
- auto operator=(const field&) -> field& deleted constexpr
- Deleted copy assignment operator.
- auto operator=(field&&) -> field& defaulted constexpr
- Defaulted move assignment operator.
-
auto def() const -> const field_
definition& constexpr - Reference to the Field definition.
-
template<typename Ident>auto identifier() const -> Ident constexpr
- Field definition identifier.
-
auto type() const -> field_
type constexpr - Type of the field.
- auto enum_type() const -> const bn::optional<bn::type_id_t>& constexpr
- Enum type of the field.
- auto has_value() const -> bool constexpr
- If this field has a value or not.
-
template<typename T>auto get() const -> T constexpr
- Extract the concrete object from the field.
Function documentation
template<typename Ident>
Ident ldtk::
Field definition identifier.
| Template parameters | |
|---|---|
| Ident | Either gen::level_field_ident or gen::entity_field_ident, depending on where this field belongs |
bool ldtk::
If this field has a value or not.
template<typename T>
T ldtk::
Extract the concrete object from the field.
| Template parameters | |
|---|---|
| T | Type of the field to be extracted. |
Type parameter T depends on your LDtk level/entity field type.
If it is a non-array type, you use one of these type:
| LDtk non-array type | Butano type T |
|---|---|
| Integer | INT (Various integer types, see below) |
| Float | bn::fixed |
| Boolean | bool |
| String | bn::string_view |
| Multilines | bn::string_view |
| Color | bn::color |
Enum (enum_name) | ldtk::gen::enum_name |
| Entity ref | ldtk:: |
| Point | bn::point |
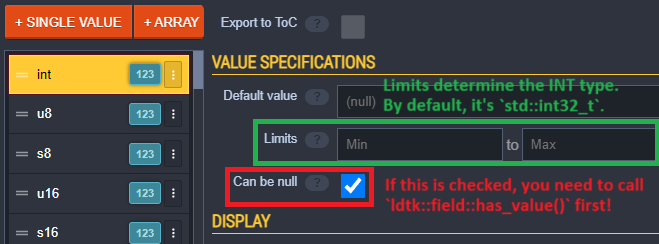
If the field is set to Can be null/Is optional in the LDtk field value specifications, (See the image below)
you must check has_ before calling get().
INT is determined by the limits you set in the LDtk field value specifications. (See the image below)
By default, if you don't set any limit, it uses std::int32_t.
If you set the Min and/or Max, it uses other integer types:
Limits [Min..Max] | INT |
|---|---|
[0..255] | std::uint8_t |
[-128..127] | std::int8_t |
[0..65535] | std::uint16_t |
[-32768..32767] | std::int16_t |
[0..4294967295] | std::uint32_t |
[-2147483648..2147483647] | std::int32_t |
[0..18446744073709551615] | std::uint64_t |
[-9223372036854775808..9223372036854775807] | std::int64_t |
- Unsigned always takes precedence over the same size of signed integer type, whenever possible.
[0..127]will bestd::uint8_t, not signed.
- Unspecified limits are assumed as
-2147483648forMinand2147483647forMax. - LDtk 1.5.3 has a bug that if you don't specify the limits, it limits putting the value in
[-32768..32767]range.- You can expand this by setting the limits yourself.
- Still, it overflows for the limits out of
[-2147483..2147483], so there's no way to usestd::uint64_tandstd::int64_tat the moment.
If it is an array type, you also need to consider if it is set to Can contain nulls in the LDtk field value specifications:
| LDtk array type | T when CAN'T contain nulls | T when CAN contain nulls |
|---|---|---|
| Integer | bn::span<const INT> | bn::span<const bn::optional<INT>> |
| Float | bn::span<const bn::fixed> | bn::span<const bn::optional<bn::fixed>> |
| Boolean | bn::span<const bool> | bn::span<const bn::optional<bool>> |
| String | bn::span<const bn::string_view> | bn::span<const bn::optional<bn::string_view>> |
| Multilines | bn::span<const bn::string_view> | bn::span<const bn::optional<bn::string_view>> |
| Color | bn::span<const bn::color> | bn::span<const bn::optional<bn::color>> |
Enum (enum_name) | bn::span<const ldtk::gen::enum_name> | bn::span<const bn::optional<ldtk::gen::enum_name>> |
| Entity ref | bn::span<const ldtk:: | bn::span<const bn::optional<ldtk:: |
| Point | bn::span<const bn::point> | bn::span<const bn::optional<bn::point>> |
For arrays, checking has_ is not necessary, as it always returns true.